WHAT ARE ARCHITECTURAL AND STRUCTURAL PROJECTS?
Architectural and structural projects are two distinct disciplines that form the foundation of the design and construction process of a building. When constructing a structure, it is essential to consider aesthetics, functionality, and safety together. At this point, architectural and structural projects emerge as two complementary and indispensable studies.
ARCHITECTURAL PROJECT
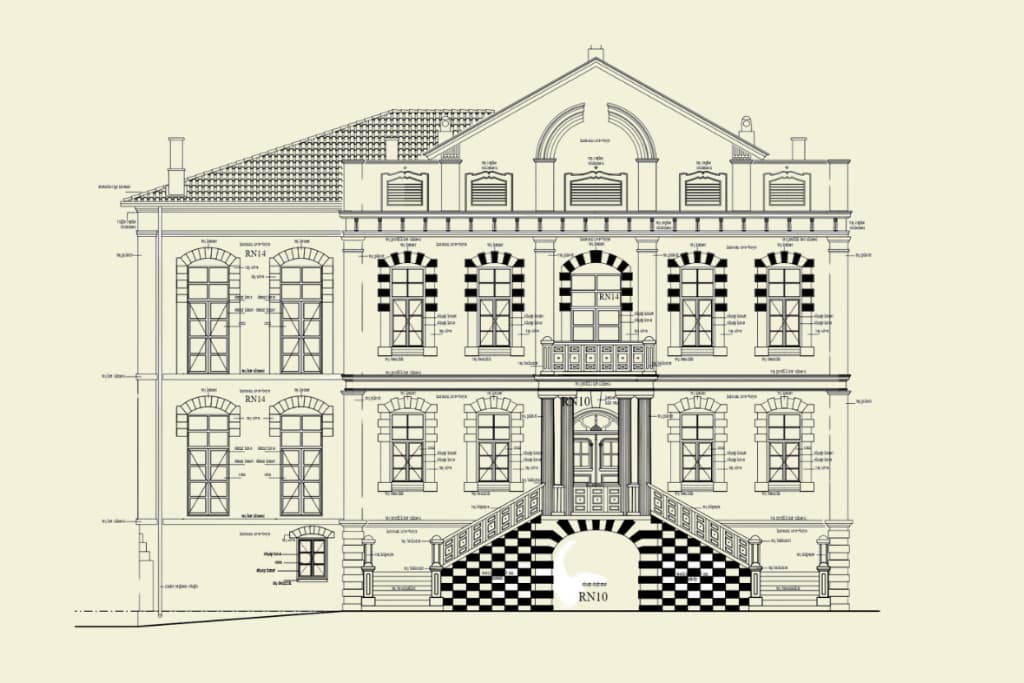
1. What is an Architectural Project?
An architectural project is a design that considers the functionality, aesthetic values, user needs, and environmental harmony of a structure. It includes technical and visual details and serves to improve user experience and optimize spatial arrangements. Architectural projects are not just drawings; they are the outcome of a design process. This process takes into account aesthetics, ergonomics, sustainability, environmental compatibility, and compliance with local regulations.
2. Importance of Architectural Projects
- Aesthetics: Enhances the visual appeal of a structure and offers a design that harmonizes with its surroundings.
- Functionality: Optimizes spaces to best meet user needs.
- Sustainability: Reduces the environmental impact of structures through energy efficiency and the use of eco-friendly materials.
- Compliance: Ensures adherence to local regulations, simplifying legal procedures.
STRUCTURAL PROJECT
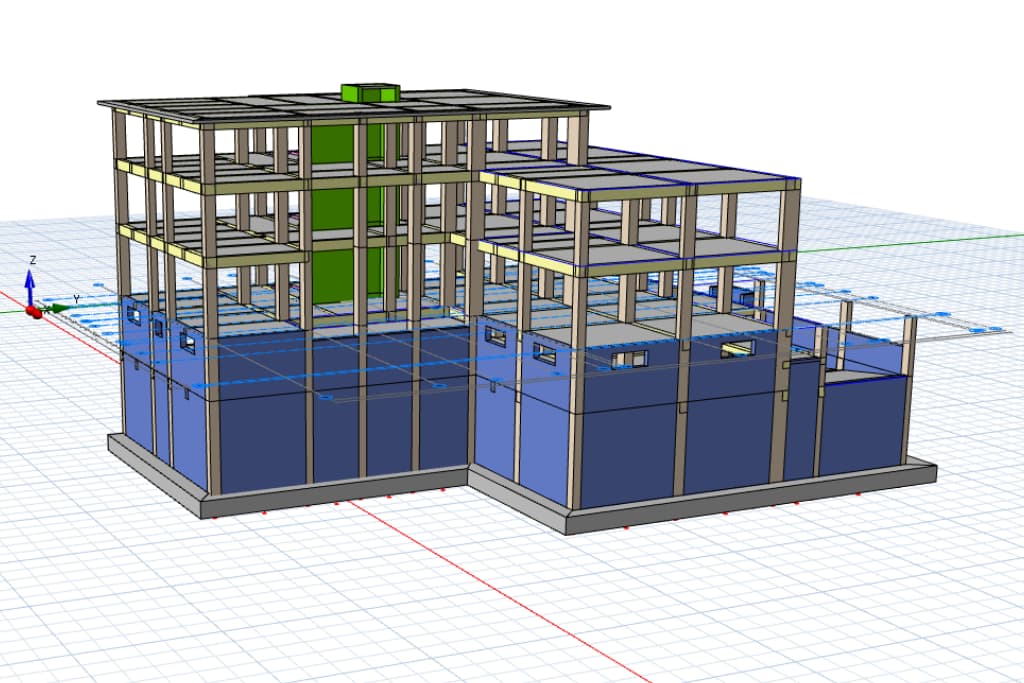
1. What is a Structural Project?
A structural project involves the design and calculations of all the load-bearing elements of a structure. This engineering work ensures the building’s stability and safety. The structural project calculates the resistance of the structure to external forces such as earthquakes, wind, snow loads, and other factors, ensuring long-term safety and durability.
2. Stages of a Structural Project
a) Soil Study
- Analyzes the ground on which the structure will be built.
- Determines soil bearing capacity, groundwater level, and other geotechnical parameters.
b) Selection of Load-Bearing System
- Chooses the type of structural system, such as reinforced concrete, steel, timber, or hybrid systems.
- Selects the most suitable system based on the structure’s function and material usage.
c) Calculations
- Structural Analysis: Analyzes loads (dead loads, live loads, earthquake, wind, snow, etc.) affecting the structure.
- Material Strength: Calculates the strength of materials like concrete, steel, timber, etc.
- Dimensioning Load-Bearing Elements: Calculates dimensions and cross-sections of columns, beams, slabs, and foundations.
d) Construction Drawings
- Foundation Plan: Includes the type (raft, pile, continuous footing) and dimensions of the foundation.
- Column and Beam Details: Specifies the locations, dimensions, and reinforcement details of columns and beams.
- Slab and Roof Plans: Prepares details and load capacities of slabs.
3. Importance of Structural Projects
- Safety: Ensures the building’s resistance to external forces, particularly natural disasters like earthquakes.
- Durability: Ensures structures are safe for use over many years through precise calculations.
- Cost Optimization: Prevents overuse of materials, offering an economical and efficient load-bearing system.
- Legal Requirement: Structural projects are mandatory for obtaining building permits.
Both architectural and structural projects are essential for creating structures that are functional, aesthetic, and safe, while also meeting legal and environmental requirements.